Meso- and microscale weather events, such as tornadoes, microbursts and severe thunderstorms,
usually change rapidly and have a short lifetime. The traditional mechanically scanning weather radar has difficulty in making accurate measurements of these weather events because the radar takes a long time (usually several minutes) to complete one volume scan. Missing or taking inaccurate measurements of these weather events may result in an incorrect forecast and terrible damage. Improving the scan rate and decreasing the volume scan time have become an urgent demand in weather surveillance. As such, weather radar systems that adopt a phased-array antenna, i.e. phased-array weather radar (PAWR), have been attracting more and more attention and are becoming an important trend.
PAWR has a flat panel antenna, which consists of many fixed antenna elements, and each antenna element can transmit and receive the signal. By changing the frequency or phase of the signals of all the elements, the antenna beam can be steered according to the control, i.e. electronically scanning. As the frequency or phase can be changed in several milliseconds, beam steering is very quick. This means the radar can skip the clear-air region and spend more time on the interesting weather events, leading to a higher scan rate. Since the locations of the clear region and the weather events are random and changing, the scanning strategies need to be considered and designed carefully.
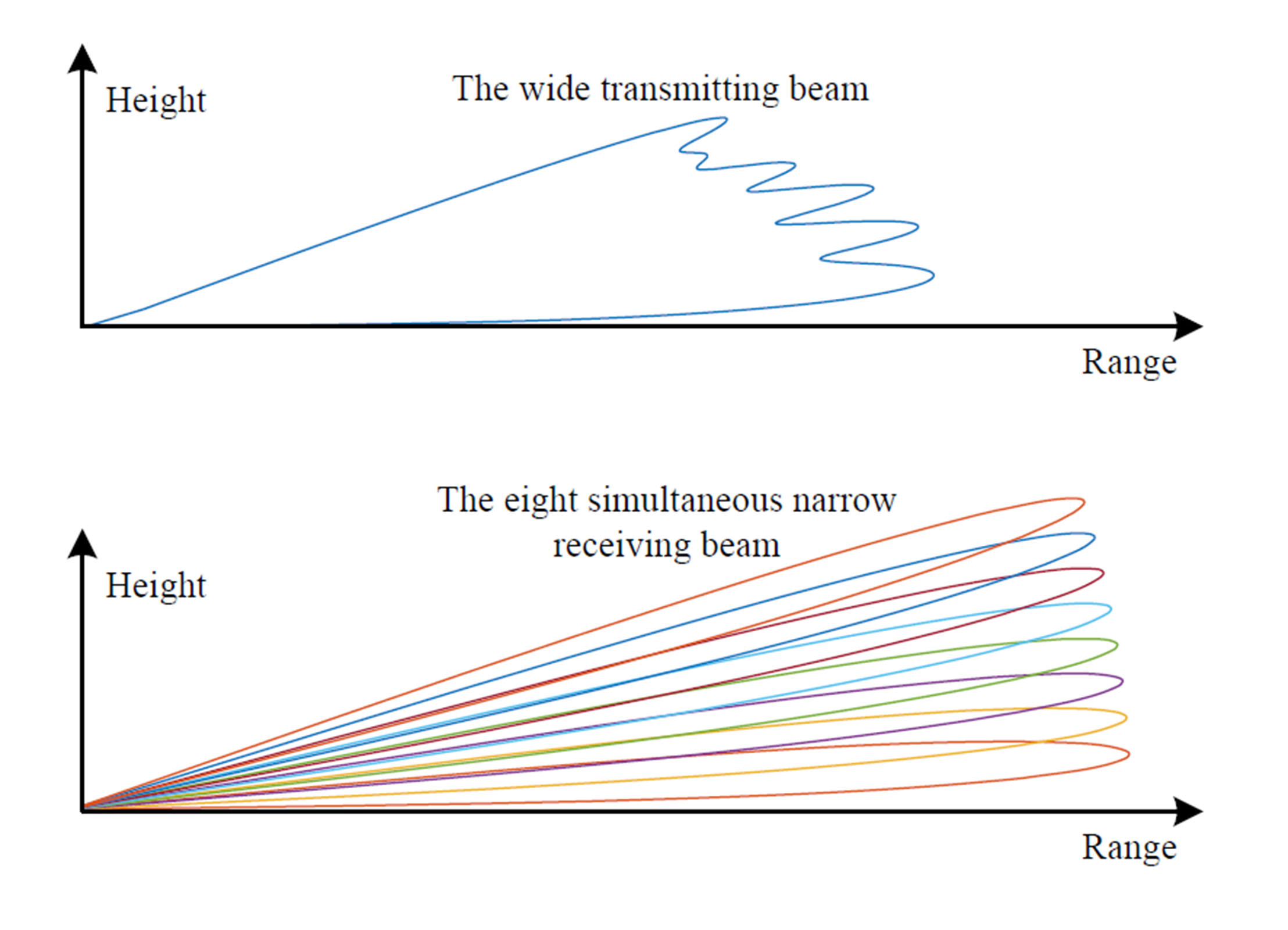
formed by the C-band PAWR based on DBF
By providing a transceiver and an A/D channel for each antenna element, the PAWR obtains the capacity for digital beamforming (DBF), which is a revolutionizing technology. DBF technology has numerous advantages including a better shaped transmitting beam, multiple simultaneous receiving beams and adaptive null formation for interference suppression. By forming one wide transmitting beam and several simultaneous narrow receiving beams in elevation, the PAWR sweeps several elevation angles in one 360° scan in azimuth. Thus the scan rate increases several times and one volume scan will take only less than a minute. This is very helpful to detect, measure and forecast the meso- and microscale weather events.
Fast scanning
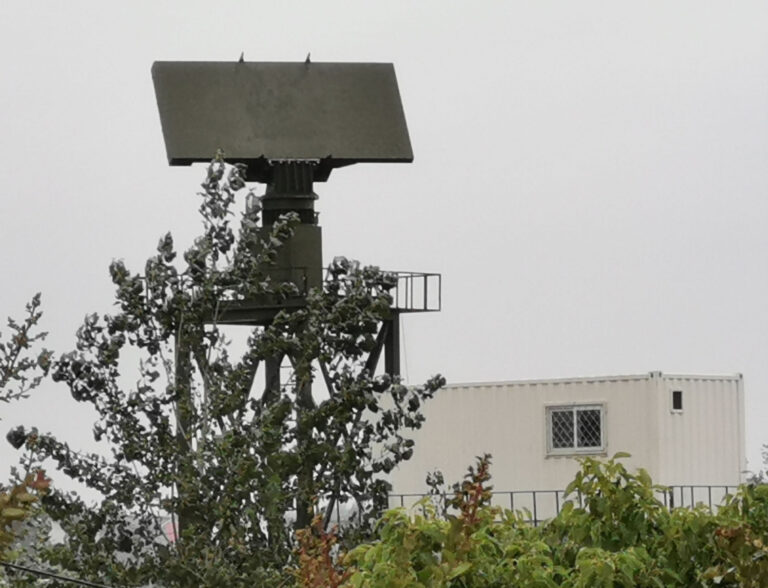
Supported by the tornado detection radar project, a C-band PAWR designed and manufactured by Aerospace Newsky Technology Company has been installed in Jiangsu Province close to Gaoyou Lake where tornadoes happen most frequently in China. The radar consists of an antenna tower and a square cabin. The antenna, T/R module and azimuth servo are on the antenna tower, and the data processing, display and console are in the square cabin. The radar scans electronically in elevation and mechanically in azimuth, which gives a balance between cost and performance. It is an element-level digital array and has the ability to perform digital beamforming. The radar can form up to eight receiving beams simultaneously. The volume scan can be completed in less than one minute. Maximum detection range is about 200km (125 miles). The radar uses pulsed compression technology and can reach 150m (492ft) spatial resolution.
PAWR has some disadvantages that must be overcome: the amplitude and phase consistency must be guaranteed or the performance will deteriorate greatly; the antenna gain and beam width change with the scanning angle; the radar sensitivity decreases if a wide transmitting beam is formed. To make the best use of PAWR, methods and technologies for radar calibration, scan strategies and other aspects of PAWR are under study.
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFE0206900).
This article was originally published in the September 2020 issue of Meteorological Technology International



