One of the most feared effects of global warming is the rise in sea level caused by the melting of polar continental ice. The scientific community relies on sampling the remote regions of the Arctic and Antarctic continental shelves to estimate these risks. They can then use these measurements to model and understand the processes that drive the melting of ice at these locations and determine the extent of meltwater that will eventually flow out from the glacier over time.
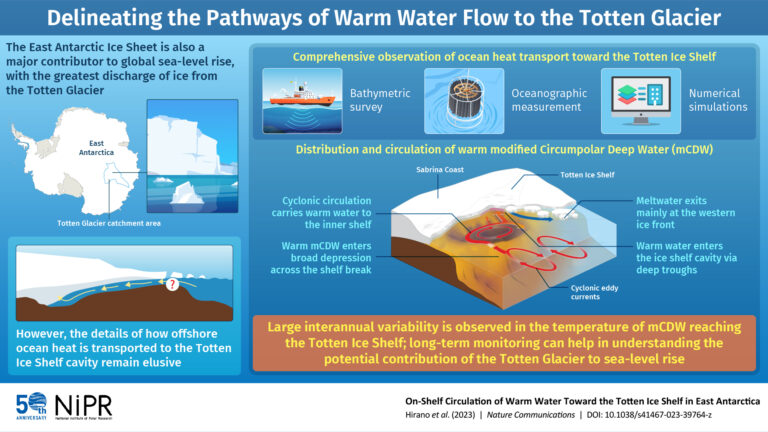
The East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which includes the Totten Glacier, is a significant contributor to ice discharge and global sea-level rise. The Totten Glacier is grounded below the surface of the ocean and is thought to contain enough ice to cause a global sea-level rise of more than 3.5m. This makes it particularly vulnerable to the influence of oceanic processes that result in ocean heat transportation, also known as ‘ocean forcing’. Unfortunately, thick sea ice cover on the Totten embayment has made it difficult to sample or observe the continental shelf near the Totten Glacier. As a result, little is known about the specifics of how offshore ocean heat reaches the ice shelf cavity beneath the glacier.
By providing additional insights and defining the pathways of ocean heat transportation into the Totten Ice Shelf cavity, a multinational team of researchers led by assistant professor Daisuke Hirano from the National Institute of Polar Research (NIPR) in Japan have now filled this knowledge gap.
The researchers used a wide variety of techniques to gather data from the Totten embayment over the course of several years. This included helicopter-based measurements, comprehensive scans of the topography of the ocean floor (bathymetry) and sea-water sampling. They combined this data with other existing measurements to extend and update a bathymetric data set, which enabled them to develop a model describing the interactions between the ocean and the Totten Ice Shelf. Using observations and numerical simulations, the researchers then estimated the water and heat circulation toward the Totten Ice Shelf cavity, the resulting melting rates and the effects of bathymetry on the entire process.
The analyses revealed crucial details about how warm offshore-origin circumpolar deep water interacts with the Totten Ice Shelf and brings in heat, accelerating melting processes. The researchers found that a train of cyclonic eddy currents brings offshore warm water toward the continental shelf break, where it enters a broad depression on the inner side. This warm water circulates within the depression and finally accesses the cavity of the Totten Ice Shelf via two large, deep glacial troughs. Finally, the basal meltwater caused by the inflow and subsequent mixing of the warm water exits the area through the western ice front of the glacier.
“The combination of comprehensive observations and model simulations enabled us to delineate the pathways of offshore warm water from the shelf break to the Totten Ice Shelf cavity and provide additional insights,” explained Hirano. “The results highlight the importance of bathymetry and regional circulation in regulating ocean heat transportation toward the ice shelf cavity.”
The findings of this study will help researchers make more accurate predictions about the state of the East Antarctic in the face of climate change. “This study provides fundamental and valuable insights into the physical processes that control the melt rate of the Totten Glacier,” continued Hirano. “The findings also emphasize that long-term monitoring will be needed to determine the sensitivity of the Totten Glacier owing to its potentially large contribution to sea-level rise.”
For more on climate measurement, please click here.